基于headscale v26.01实现异地组网
1.服务器环境
Linux 5.4.0-216-generic #236-Ubuntu SMP Fri Apr 11 19:53:21 UTC 2025 x86_64 GNU/Linux
镜像获取
2.修改软件源以及安装基本软件
sudo cp -rf /etc/apt/sources.list /etc/apt/sources.list.bak
sudo rm -rf /etc/apt/sources.list
sudo vi /etc/apt/sources.list填入以下源:
##中科大源
deb https://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/ubuntu/ bionic main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src https://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/ubuntu/ bionic main restricted universe multiverse
deb https://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/ubuntu/ bionic-updates main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src https://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/ubuntu/ bionic-updates main restricted universe multiverse
deb https://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/ubuntu/ bionic-backports main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src https://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/ubuntu/ bionic-backports main restricted universe multiverse
deb https://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/ubuntu/ bionic-security main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src https://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/ubuntu/ bionic-security main restricted universe multiverse
deb https://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/ubuntu/ bionic-proposed main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src https://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/ubuntu/ bionic-proposed main restricted universe multiversewq!保存,然后执行
sudo apt update
sudo apt install vim wget curl -y3.创建存放目录
sudo mkdir -p /www/wwwroot/[你的域名]
# [你的域名] 改成你自己的
cd /www/wwwroot/[你的域名]
# 同上4.下载headscale
代码仓库
终端加速github
sudo vim /etc/hosts在127.0.0.1的下面一行复制以下内容
31.13.76.65 github.global.ssl.fastly.net
20.205.243.166 github.com
185.199.108.154 github.githubassets.com
185.199.108.133 objects.githubusercontent.comwq!保存,然后再运行:
sudo systemctl restart systemd-resolved
sudo wget -O headscale https://github.com/juanfont/headscale/releases/download/v0.26.1/headscale_0.26.1_linux_amd64
sudo chmod +x headscale
sudo ln -s /www/wwwroot/[你的域名]/headscale /usr/local/bin/headscale
# 创建软连接
headscale version
# 验证版本应看到以下输出:
yuos@test:/www/wwwroot/[你的域名]$ headscale version
0.26.15.创建专网用户&配置文件
1.创建用户
useradd -r -m -d /var/lib/headscale -s /usr/sbin/nologin headscale赋予所有权:
chown -R headscale:headscale /www/wwwroot/[你的域名]2.创建数据文件
# 创建运行时目录(与服务文件中的RuntimeDirectory对应)
mkdir -p /var/run/headscale/
# 在你的工作目录下创建SQLite数据库文件和derp配置文件
touch /www/wwwroot/[你的域名]/db.sqlite /www/wwwroot/[你的域名]/derp.yaml
# 授权权限(匹配服务文件中设置的工作目录和运行时目录)
chown -R headscale:headscale /var/run/headscale/ /www/wwwroot/[你的域名]
3.创建配置文件
cd /www/wwwroot/[你的域名]
wget https://github.com/juanfont/headscale/raw/main/config-example.yaml -O config.yaml
# 在你的工作目录下下载官方示例配置
chown headscale:headscale /www/wwwroot/[你的域名]/config.yaml
# 确保 headscale 用户对配置文件有读写权限
chmod a+r /www/wwwroot/[你的域名]/config.yaml /www/wwwroot/[你的域名]/derp.yaml
# 赋予所有用户读取权限(符合之前的操作逻辑)4.修改配置文件
mkdir -p /www/wwwroot/[你的域名]/tls
mkdir -p /www/wwwroot/[你的域名]/ssl
nano config.yamlPS:证书申请可以到[腾讯云](https://console.cloud.tencent.com/ssl)免费申请
示例:
---
# headscale will look for a configuration file named `config.yaml` (or `config.json`) in the following order:
#
# - `/etc/headscale`
# - `~/.headscale`
# - current working directory
# The url clients will connect to.
# Typically this will be a domain like:
#
# https://myheadscale.example.com:443
#
server_url: http://[ip]:8080
# Address to listen to / bind to on the server
#
# For production:
# listen_addr: 0.0.0.0:8080
listen_addr: [ip]:8080
# Address to listen to /metrics and /debug, you may want
# to keep this endpoint private to your internal network
metrics_listen_addr: [ip]:8081
# Address to listen for gRPC.
# gRPC is used for controlling a headscale server
# remotely with the CLI
# Note: Remote access _only_ works if you have
# valid certificates.
#
# For production:
# grpc_listen_addr: 0.0.0.0:50443
grpc_listen_addr: [ip]:8082
# Allow the gRPC admin interface to run in INSECURE
# mode. This is not recommended as the traffic will
# be unencrypted. Only enable if you know what you
# are doing.
grpc_allow_insecure: false
# The Noise section includes specific configuration for the
# TS2021 Noise protocol
noise:
# The Noise private key is used to encrypt the traffic between headscale and
# Tailscale clients when using the new Noise-based protocol. A missing key
# will be automatically generated.
private_key_path: /www/wwwroot/[你的域名]/noise_private.key
# List of IP prefixes to allocate tailaddresses from.
# Each prefix consists of either an IPv4 or IPv6 address,
# and the associated prefix length, delimited by a slash.
# It must be within IP ranges supported by the Tailscale
# client - i.e., subnets of 100.64.0.0/10 and fd7a:115c:a1e0::/48.
# See below:
# IPv6: https://github.com/tailscale/tailscale/blob/22ebb25e833264f58d7c3f534a8b166894a89536/net/tsaddr/tsaddr.go#LL81C52-L81C71
# IPv4: https://github.com/tailscale/tailscale/blob/22ebb25e833264f58d7c3f534a8b166894a89536/net/tsaddr/tsaddr.go#L33
# Any other range is NOT supported, and it will cause unexpected issues.
prefixes:
v4: 100.88.0.0/16
#v6: fd7a:115c:a1e0::/48
# Strategy used for allocation of IPs to nodes, available options:
# - sequential (default): assigns the next free IP from the previous given IP.
# - random: assigns the next free IP from a pseudo-random IP generator (crypto/rand).
allocation: sequential
# DERP is a relay system that Tailscale uses when a direct
# connection cannot be established.
# https://tailscale.com/blog/how-tailscale-works/#encrypted-tcp-relays-derp
#
# headscale needs a list of DERP servers that can be presented
# to the clients.
derp:
server:
# If enabled, runs the embedded DERP server and merges it into the rest of the DERP config
# The Headscale server_url defined above MUST be using https, DERP requires TLS to be in place
enabled: false
# Region ID to use for the embedded DERP server.
# The local DERP prevails if the region ID collides with other region ID coming from
# the regular DERP config.
region_id: 999
# Region code and name are displayed in the Tailscale UI to identify a DERP region
region_code: "headscale"
region_name: "Headscale Embedded DERP"
# Only allow clients associated with this server access
verify_clients: true
# Listens over UDP at the configured address for STUN connections - to help with NAT traversal.
# When the embedded DERP server is enabled stun_listen_addr MUST be defined.
#
# For more details on how this works, check this great article: https://tailscale.com/blog/how-tailscale-works/
stun_listen_addr: "0.0.0.0:[UDP打洞端口]"
# Private key used to encrypt the traffic between headscale DERP and
# Tailscale clients. A missing key will be automatically generated.
private_key_path: /www/wwwroot/[你的域名]/ssl/[derp域名].key
# This flag can be used, so the DERP map entry for the embedded DERP server is not written automatically,
# it enables the creation of your very own DERP map entry using a locally available file with the parameter DERP.paths
# If you enable the DERP server and set this to false, it is required to add the DERP server to the DERP map using DERP.paths
automatically_add_embedded_derp_region: true
# For better connection stability (especially when using an Exit-Node and DNS is not working),
# it is possible to optionally add the public IPv4 and IPv6 address to the Derp-Map using:
ipv4: [ip]
ipv6: [ipv6]
# List of externally available DERP maps encoded in JSON
urls:
- https://controlplane.tailscale.com/derpmap/default
# Locally available DERP map files encoded in YAML
#
# This option is mostly interesting for people hosting
# their own DERP servers:
# https://tailscale.com/kb/1118/custom-derp-servers/
#
# paths:
# - /etc/headscale/derp-example.yaml
paths:
- /www/wwwroot/[你的域名]/derp.yaml
# If enabled, a worker will be set up to periodically
# refresh the given sources and update the derpmap
# will be set up.
auto_update_enabled: true
# How often should we check for DERP updates?
update_frequency: 24h
# Disables the automatic check for headscale updates on startup
disable_check_updates: false
# Time before an inactive ephemeral node is deleted?
ephemeral_node_inactivity_timeout: 30m
database:
# Database type. Available options: sqlite, postgres
# Please note that using Postgres is highly discouraged as it is only supported for legacy reasons.
# All new development, testing and optimisations are done with SQLite in mind.
type: sqlite
# Enable debug mode. This setting requires the log.level to be set to "debug" or "trace".
debug: false
# GORM configuration settings.
gorm:
# Enable prepared statements.
prepare_stmt: true
# Enable parameterized queries.
parameterized_queries: true
# Skip logging "record not found" errors.
skip_err_record_not_found: true
# Threshold for slow queries in milliseconds.
slow_threshold: 1000
# SQLite config
sqlite:
path: /www/wwwroot/[你的域名]/db.sqlite
# Enable WAL mode for SQLite. This is recommended for production environments.
# https://www.sqlite.org/wal.html
write_ahead_log: true
# Maximum number of WAL file frames before the WAL file is automatically checkpointed.
# https://www.sqlite.org/c3ref/wal_autocheckpoint.html
# Set to 0 to disable automatic checkpointing.
wal_autocheckpoint: 1000
# # Postgres config
# Please note that using Postgres is highly discouraged as it is only supported for legacy reasons.
# See database.type for more information.
# postgres:
# # If using a Unix socket to connect to Postgres, set the socket path in the 'host' field and leave 'port' blank.
# host: localhost
# port: 5432
# name: headscale
# user: foo
# pass: bar
# max_open_conns: 10
# max_idle_conns: 10
# conn_max_idle_time_secs: 3600
# # If other 'sslmode' is required instead of 'require(true)' and 'disabled(false)', set the 'sslmode' you need
# # in the 'ssl' field. Refers to https://www.postgresql.org/docs/current/libpq-ssl.html Table 34.1.
# ssl: false
### TLS configuration
#
## Let's encrypt / ACME
#
# headscale supports automatically requesting and setting up
# TLS for a domain with Let's Encrypt.
#
# URL to ACME directory
acme_url: https://acme-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directory
# Email to register with ACME provider
acme_email: ""
# Domain name to request a TLS certificate for:
tls_letsencrypt_hostname: ""
# Path to store certificates and metadata needed by
# letsencrypt
# For production:
tls_letsencrypt_cache_dir: /var/lib/headscale/cache
# Type of ACME challenge to use, currently supported types:
# HTTP-01 or TLS-ALPN-01
# See: docs/ref/tls.md for more information
tls_letsencrypt_challenge_type: HTTP-01
# When HTTP-01 challenge is chosen, letsencrypt must set up a
# verification endpoint, and it will be listening on:
# :http = port 80
tls_letsencrypt_listen: ":http"
## Use already defined certificates:
tls_cert_path: "/www/wwwroot/[你的域名]/tls/[你的域名].crt"
tls_key_path: "/www/wwwroot/[你的域名]/tls/[你的域名].key"
log:
# Valid log levels: panic, fatal, error, warn, info, debug, trace
level: info
# Output formatting for logs: text or json
format: text
## Policy
# headscale supports Tailscale's ACL policies.
# Please have a look to their KB to better
# understand the concepts: https://tailscale.com/kb/1018/acls/
policy:
# The mode can be "file" or "database" that defines
# where the ACL policies are stored and read from.
mode: file
# If the mode is set to "file", the path to a
# HuJSON file containing ACL policies.
path: ""
## DNS
#
# headscale supports Tailscale's DNS configuration and MagicDNS.
# Please have a look to their KB to better understand the concepts:
#
# - https://tailscale.com/kb/1054/dns/
# - https://tailscale.com/kb/1081/magicdns/
# - https://tailscale.com/blog/2021-09-private-dns-with-magicdns/
#
# Please note that for the DNS configuration to have any effect,
# clients must have the `--accept-dns=true` option enabled. This is the
# default for the Tailscale client. This option is enabled by default
# in the Tailscale client.
#
# Setting _any_ of the configuration and `--accept-dns=true` on the
# clients will integrate with the DNS manager on the client or
# overwrite /etc/resolv.conf.
# https://tailscale.com/kb/1235/resolv-conf
#
# If you want stop Headscale from managing the DNS configuration
# all the fields under `dns` should be set to empty values.
dns:
# Whether to use [MagicDNS](https://tailscale.com/kb/1081/magicdns/).
magic_dns: false
# Defines the base domain to create the hostnames for MagicDNS.
# This domain _must_ be different from the server_url domain.
# `base_domain` must be a FQDN, without the trailing dot.
# The FQDN of the hosts will be
# `hostname.base_domain` (e.g., _myhost.example.com_).
base_domain: [你的域名]
# Whether to use the local DNS settings of a node (default) or override the
# local DNS settings and force the use of Headscale's DNS configuration.
override_local_dns: false
# List of DNS servers to expose to clients.
nameservers:
global:
- 1.1.1.1
- 223.5.5.5
- 2606:4700:4700::1111
- 2606:4700:4700::1001
# NextDNS (see https://tailscale.com/kb/1218/nextdns/).
# "abc123" is example NextDNS ID, replace with yours.
# - https://dns.nextdns.io/abc123
# Split DNS (see https://tailscale.com/kb/1054/dns/),
# a map of domains and which DNS server to use for each.
split:
{}
# foo.bar.com:
# - 1.1.1.1
# darp.headscale.net:
# - 1.1.1.1
# - 8.8.8.8
# Set custom DNS search domains. With MagicDNS enabled,
# your tailnet base_domain is always the first search domain.
search_domains: []
# Extra DNS records
# so far only A and AAAA records are supported (on the tailscale side)
# See: docs/ref/dns.md
extra_records: []
# - name: "grafana.myvpn.example.com"
# type: "A"
# value: "100.64.0.3"
#
# # you can also put it in one line
# - { name: "prometheus.myvpn.example.com", type: "A", value: "100.64.0.3" }
#
# Alternatively, extra DNS records can be loaded from a JSON file.
# Headscale processes this file on each change.
# extra_records_path: /var/lib/headscale/extra-records.json
# Unix socket used for the CLI to connect without authentication
# Note: for production you will want to set this to something like:
unix_socket: /var/run/headscale/headscale.sock
unix_socket_permission: "0770"
# OpenID Connect
# oidc:
# # Block startup until the identity provider is available and healthy.
# only_start_if_oidc_is_available: true
#
# # OpenID Connect Issuer URL from the identity provider
# issuer: "https://your-oidc.issuer.com/path"
#
# # Client ID from the identity provider
# client_id: "your-oidc-client-id"
#
# # Client secret generated by the identity provider
# # Note: client_secret and client_secret_path are mutually exclusive.
# client_secret: "your-oidc-client-secret"
# # Alternatively, set `client_secret_path` to read the secret from the file.
# # It resolves environment variables, making integration to systemd's
# # `LoadCredential` straightforward:
# client_secret_path: "${CREDENTIALS_DIRECTORY}/oidc_client_secret"
#
# # The amount of time a node is authenticated with OpenID until it expires
# # and needs to reauthenticate.
# # Setting the value to "0" will mean no expiry.
# expiry: 180d
#
# # Use the expiry from the token received from OpenID when the user logged
# # in. This will typically lead to frequent need to reauthenticate and should
# # only be enabled if you know what you are doing.
# # Note: enabling this will cause `oidc.expiry` to be ignored.
# use_expiry_from_token: false
#
# # The OIDC scopes to use, defaults to "openid", "profile" and "email".
# # Custom scopes can be configured as needed, be sure to always include the
# # required "openid" scope.
# scope: ["openid", "profile", "email"]
#
# # Provide custom key/value pairs which get sent to the identity provider's
# # authorization endpoint.
# extra_params:
# domain_hint: example.com
#
# # Only accept users whose email domain is part of the allowed_domains list.
# allowed_domains:
# - example.com
#
# # Only accept users whose email address is part of the allowed_users list.
# allowed_users:
# - alice@example.com
#
# # Only accept users which are members of at least one group in the
# # allowed_groups list.
# allowed_groups:
# - /headscale
#
# # Optional: PKCE (Proof Key for Code Exchange) configuration
# # PKCE adds an additional layer of security to the OAuth 2.0 authorization code flow
# # by preventing authorization code interception attacks
# # See https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/html/rfc7636
# pkce:
# # Enable or disable PKCE support (default: false)
# enabled: false
#
# # PKCE method to use:
# # - plain: Use plain code verifier
# # - S256: Use SHA256 hashed code verifier (default, recommended)
# method: S256
# Logtail configuration
# Logtail is Tailscales logging and auditing infrastructure, it allows the control panel
# to instruct tailscale nodes to log their activity to a remote server.
logtail:
# Enable logtail for this headscales clients.
# As there is currently no support for overriding the log server in headscale, this is
# disabled by default. Enabling this will make your clients send logs to Tailscale Inc.
enabled: false
# Enabling this option makes devices prefer a random port for WireGuard traffic over the
# default static port 41641. This option is intended as a workaround for some buggy
# firewall devices. See https://tailscale.com/kb/1181/firewalls/ for more information.
randomize_client_port: true
5.安装和设置 headscale 补全
sudo apt update
sudo apt install -y bash-completion
headscale completion bash > /etc/bash_completion.d/headscale
. /etc/bash_completion.d/headscale启动 headscale daemon 进程:
# 测试文件
headscale configtest
# 得到以下输出:
# 2025-08-12T02:34:38+02:00 INF No private key file at path, creating... path=/www/wwwroot/[你的域名]/noise_private.key
# 2025-08-12T02:34:38+02:00 INF Opening database database=sqlite3 path=/www/wwwroot/[你的域名]/db.sqlite
# 2025-08-12T02:34:39+02:00 INF Using policy manager version: 2
headscale serve
# 配置文件没问题就 ctrl +c 取消掉稍后使用 systemd 启动
chown -R headscale:headscale /var/lib/headscale
systemctl daemon-reload6.配置系统服务
sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/headscale.service写入以下内容:
[Unit]
Description=headscale service
After=network.target
After=syslog.target
Documentation=https://github.com/juanfont/headscale
[Service]
Type=simple
# 使用专用的headscale用户和组(需先创建)
User=headscale
Group=headscale
# 你的headscale执行路径
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/headscale serve
Restart=always
RestartSec=5
Environment=PATH=/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin
# 安全增强配置
NoNewPrivileges=yes
PrivateTmp=yes
ProtectSystem=strict
ProtectHome=yes
# 你的工作目录
WorkingDirectory=/www/wwwroot/[你的域名]
# 允许读写的路径(根据你的实际路径调整)
ReadWritePaths=/www/wwwroot/[你的域名] /var/run/headscale
AmbientCapabilities=CAP_NET_BIND_SERVICE
RuntimeDirectory=headscale
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.targetsudo systemctl daemon-reload
# 重新加载 systemd 配置7.搭建derp服务
1.查看机器上的 iptables 模式
下面的 tailscale 需要设置 firewall-mode 为 iptables 或者 nftables,但是需要和主机输出一致。
iptables -w -V得到输出:iptables v1.8.4 (legacy),就设置iptables
iptables -w -V得到输出:iptables v1.8.7 (nf_tables),就设置nftables
2.安装docker
3.创建docker compose文件
cat > docker-compose.yml << EOF
services:
# https://tailscale.com/kb/1282/docker
tailscale:
hostname: tailscale
container_name: tailscale
restart: unless-stopped
network_mode: host
image: docker.m.daocloud.io/tailscale/tailscale:v1.86.2
#image: tailscale/tailscale:unstable
cap_add:
- NET_ADMIN
- NET_RAW
- sys_module
volumes:
- /usr/share/zoneinfo/Asia/Shanghai:/etc/localtime:ro
- /lib/modules:/lib/modules
- /run/xtables.lock:/run/xtables.lock:rw
- /var/run/tailscale/:/var/run/tailscale/
- ./tailscale:/var/lib/tailscale
devices:
- /dev/net/tun:/dev/net/tun
environment:
TS_EXTRA_ARGS: --advertise-tags=tag:container
TS_AUTH_ONCE: "true"
TS_HOSTNAME: ecs
TS_USERSPACE: "false"
# 禁用收集或发送任何日志数据,会发往 https://log.tailscale.io
TS_NO_LOGS_NO_SUPPORT: "true"
TS_SOCKET: "/var/run/tailscale/tailscaled.sock"
TS_STATE_DIR: /var/lib/tailscale/
#TS_LOGIN_SERVER: "http://127.0.0.1:528"
#TS_CONTROL_IS_PLAINTEXT_HTTP: "true"
TS_DEBUG_FIREWALL_MODE: iptables
# 使用和宿主机模式一致的
derper:
container_name: derper
image: fredliang/derper:v1.86.2
restart: unless-stopped
network_mode: host
volumes:
- /usr/share/zoneinfo/Asia/Shanghai:/etc/localtime:ro
# 容器生成的证书存放,如果是自己的绿锁证书,存放文件名为
# $DERP_DOMAIN.key $DERP_DOMAIN.crt
- ./ssl:/app/certs
- ./derp.yaml:/app/config.yaml:ro
- /var/run/tailscale/:/var/run/tailscale/
environment:
DERP_DOMAIN: [derp域名]
# 域名,由于不是绿锁 https,随意写,和后面 derp.yaml 一致即可
DERP_ADDR: ':[WEB面板端口]'
# https 端口
DERP_STUN_PORT: '[UDP打洞端口]'
# udp port
DERP_HTTP_PORT: '-1'
DERP_VERIFY_CLIENTS: "true"
DERP_CERT_DIR: /app/certs
depends_on:
- tailscale
EOF4.编写derp.yaml文件
cat > derp.yaml << EOF# If you plan to somehow use headscale, please deploy your own DERP infra: https://tailscale.com/kb/1118/custom-derp-servers/
regions:
900:
regionid: 900
regioncode: [节点名称]
regionname: [节点区域]
nodes:
- name: 900a
regionid: 900
hostname: [derp域名
stunport: [UDP打洞端口]
stunonly: false
derpport: [WEB面板端口]
ipv4: [IPV4]
ipv6: [IPV6]
EOF5.启动容器
docker-compose up -d8.启动服务
1.赋予权限
sudo chown -R headscale:headscale /www/wwwroot/[域名]
# 确保数据库文件可读写
sudo chmod -R 755 /www/wwwroot/[域名]2.启动服务
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
# 重新加载服务配置
sudo systemctl start headscale
# 启动 headscale 服务
sudo systemctl enable headscale
# 设置开机自启动
sudo systemctl status headscale
# 检查服务状态状态应如下:
● headscale.service - headscale service
Loaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/headscale.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Tue 2025-08-12 08:31:54 CEST; 1min 28s ago
Docs: https://github.com/juanfont/headscale
Main PID: 11738 (headscale)
Tasks: 7 (limit: 1042)
Memory: 11.1M
CGroup: /system.slice/headscale.service
└─11738 /usr/local/bin/headscale serve3.其他命令
sudo systemctl restart headscale
# 重启服务
sudo systemctl stop headscale
# 停止服务9.客户端配置
1.服务端创建 authkeys
headscale user create yuos
# 创建你自己的用户修改 yuos 为你自己的就行
headscale users list
# 列出用户ID
# 输出如下
# ID | Name | Username | Email | Created
# 1 | | yuos | | 2025-08-12 06:59:30
#使用用户 ID 创建预授权密钥
headscale preauthkeys --user 1 create --reusable --expiration 999d
# 生成一个过期时间 999d 且可以重复使用的 authkey
# 查看已经生成的 key:
headscale preauthkeys --user 1 list2.tailscale up 常用通用选项
下面是 tailscale up 时候一些常用通用选项:
- --login-server: 指定使用的中央服务器地址(必填)
- --advertise-routes: 向中央服务器报告当前客户端处于哪个内网网段下, 便于中央服务器让同内网设备直接内网直连(可选的)或者将其他设备指定流量路由到当前内网(可选),多条路由英文逗号隔开
- --accept-routes: 是否接受中央服务器下发的用于路由到其他客户端内网的路由规则(可选)
- --accept-dns: 是否使用中央服务器下发的 DNS 相关配置(可选, 推荐关闭)
- --hostname: 设置 machine name,否则默认会以 hostname 注册上去,特别安卓的 hostname 无法修改
3.服务接入
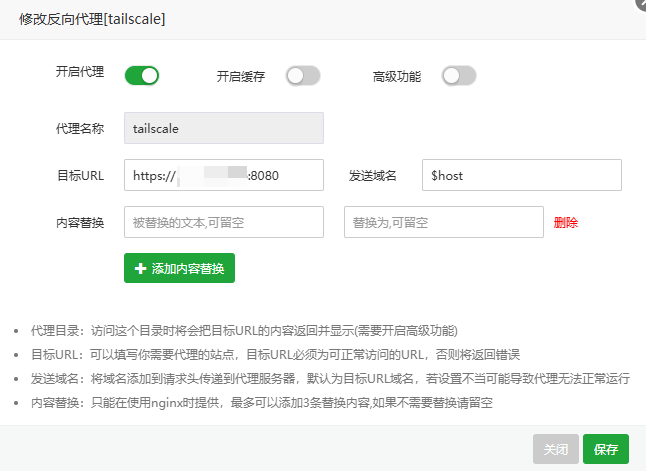
3.1 配置反向代理
#PROXY-START/
location ^~ /
{
proxy_pass http://[IP]:8080;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header REMOTE-HOST $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection $connection_upgrade;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
# 新增:告诉 Headscale 客户端使用 HTTPS
proxy_http_version 1.1;
# proxy_hide_header Upgrade;
add_header X-Cache $upstream_cache_status;
#Set Nginx Cache
set $static_fileCRZvQTwv 0;
if ( $uri ~* "\.(gif|png|jpg|css|js|woff|woff2)$" )
{
set $static_fileCRZvQTwv 1;
expires 1m;
}
if ( $static_fileCRZvQTwv = 0 )
{
add_header Cache-Control no-cache;
}
}
# 新增:处理 gRPC 请求(Tailscale 客户端核心通信)
location /grpc/ {
proxy_pass http://[IP]:8082; # 转发到 Headscale 的 gRPC 端口(默认 8082)
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
proxy_set_header Connection ""; # gRPC 不需要 Keep-Alive,清空连接头
proxy_set_header Upgrade "h2c"; # gRPC 使用 HTTP/2 明文协议(h2c)
}
#PROXY-END/补充 $connection_upgrade 变量定义,编辑 /etc/nginx/nginx.conf(或面板中的全局 Nginx 配置),在 http { ... } 内添加:
http {
# 其他现有配置...
# 新增:定义连接升级变量
map $http_upgrade $connection_upgrade {
default upgrade;
'' close;
}
}
systemctl restart nginx
# 重启 Nginx 使配置生效防火墙放行端口:
3.2 derp 接入
docker exec -ti tailscale sh
# 进入 tailscale 容器
tailscale down
# 清除旧配置
tailscale up --accept-dns=false --accept-routes --auth-key=[你的key] --hostname=derp --login-server=https://[域名] --advertise-tags=tag:container
# 继承之前的参数可以 headscale 上查看信息:
headscale -c /www/wwwroot/[域名]/config.yaml node list
docker logs -f tailscale
# 可搭配容器日志查看
headscale -c /www/wwwroot/[域名]/config.yaml node delete -i {node_id}
# 删除不需要的节点
headscale -c /www/wwwroot/[域名]/config.yaml nodes delete -i 1
# 示例
Linux 上 tailscale 会利用 tun 创建网卡,路由表在 52 里:
ip route show table 523.3 linux接入
未安装tailscale的
curl -fsSL https://tailscale.com/install.sh | sh已安装的
tailscale logout
# 退出登录
tailscale down
# 清除旧配置
sudo systemctl stop tailscaled
# 停止 Tailscale 服务
sudo rm -rf /var/lib/tailscale/*
# 删除本地存储的认证信息和配置
sudo systemctl start tailscaled
# 重启服务
tailscale up --accept-dns=false --accept-routes --auth-key=[你的key] --hostname=[设备名字] --login-server=https://[域名] --advertise-tags=tag:container
# 服务注册
tailscale netcheck
# 检查网络节点3.4 windows接入
tailscale up --accept-dns=false --accept-routes --auth-key=[你的key] --hostname=[设备名字] --login-server=https://[域名] --advertise-tags=tag:container
# 服务注册
tailscale netcheck
# 检查网络节点效果如下: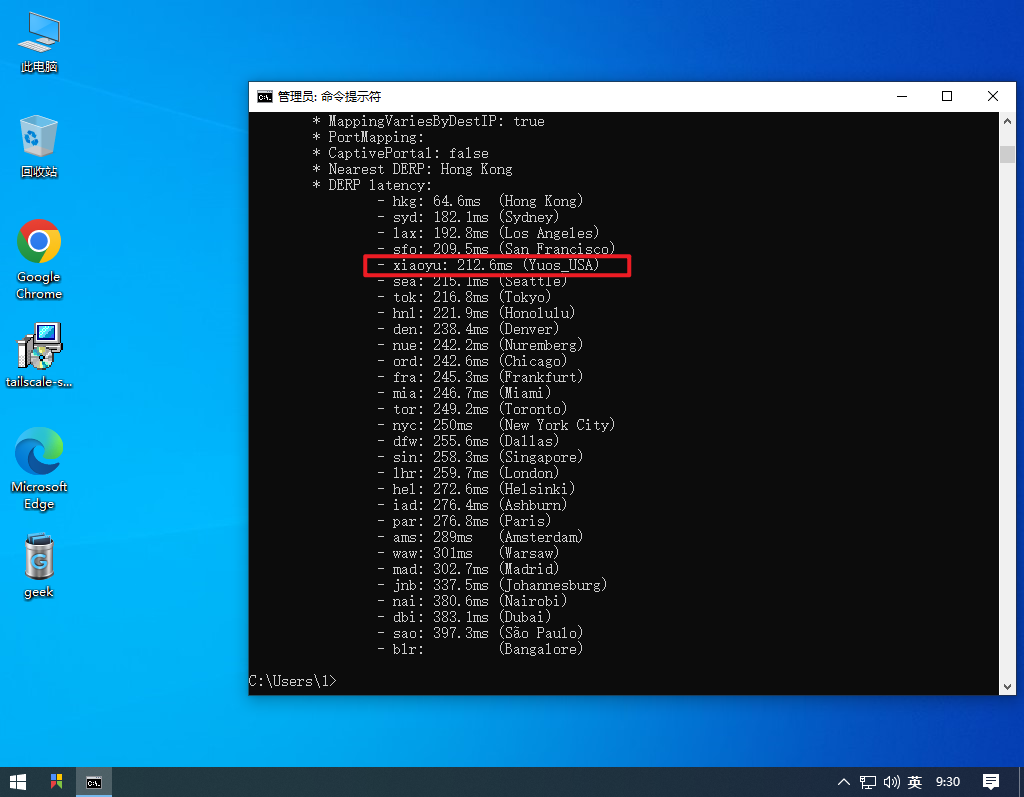
3.5 路由器openwrt接入

输入指令:
tailscale up --accept-dns=false --accept-routes --auth-key=秘钥 --hostname=设备名字 --login-server=https://wg.yuos.top --advertise-tags=tag:container
测试路由器和其他节点的连通性:
测试正常
添加新接口

去服务区查看下路由器的虚拟网IP地址
headscale -c config.yaml nodes list --user 用户名


添加自定义防火墙规则
iptables -I FORWARD -i tailscale0 -j ACCEPT
iptables -I FORWARD -o tailscale0 -j ACCEPT
iptables -t nat -I POSTROUTING -o tailscale0 -j MASQUERADE保存后重启防火墙:
终端重启路由器防火墙:
/etc/init.d/firewall restart再在局域网下ping下目标节点
ok,可以了
3.6 常用headscale命令
headscale -c /www/wwwroot/[域名]/config.yaml users list
# 列出用户
headscale -c /www/wwwroot/[域名]/config.yaml nodes list --user {user2}
# 若第二个用户存在,查看其名下的节点(替换 {user2} 为实际用户名):
headscale -c config.yaml nodes delete --identifier ID
# 删除某用户下指定节点(ID方式)
headscale -c config.yaml nodes delete --identifier ID
#删除某用户下指定节点(节点名称方式)
headscale -c /www/wwwroot/[域名]/config.yaml users delete --user user2
# 通过用户名删除指定用户
headscale -c /www/wwwroot/[域名]/config.yaml users delete --user 2
# 通过用户 ID 删除
headscale -c /www/wwwroot/[域名]/config.yaml users delete --user user2 --force
# 强制删除用户及其所有节点
headscale -c /www/wwwroot/[域名]/config.yaml users list
# 验证删除结果